Navigating the Depths: Exploring Different Types of Depression and Treatment Options
May 17, 2024
How Trauma Rewires the Brain
May 23, 2024Childhood trauma casts a long shadow, shaping the trajectory of individuals’ lives long into adulthood. But what exactly constitutes childhood trauma, and how does it manifest in the lives of survivors? In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of childhood trauma, its various forms, and the journey toward healing and resilience.
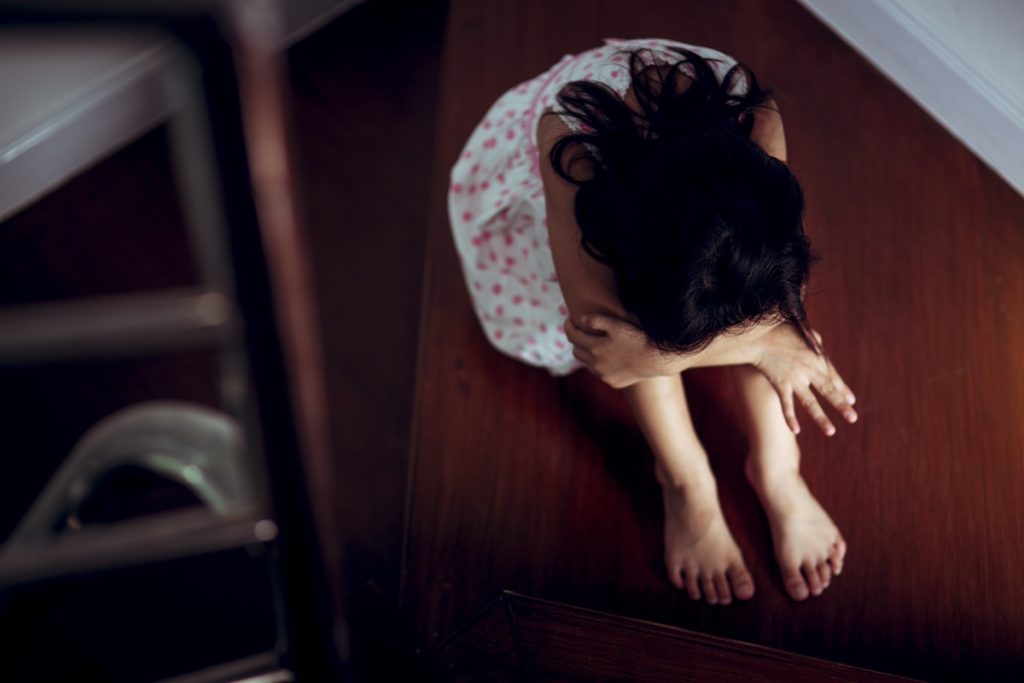

What is Childhood Trauma?
Childhood trauma encompasses a range of adverse experiences that occur during formative years, disrupting normal development and leaving lasting psychological and emotional scars. These experiences may include physical, emotional, or sexual abuse; neglect; household dysfunction such as substance abuse or domestic violence; and other forms of adversity that threaten a child’s sense of safety, security, and well-being.
Unlike ordinary childhood stressors, which are temporary and manageable within the context of supportive relationships, childhood trauma overwhelms a child’s coping mechanisms, leaving them vulnerable to profound and enduring effects on their physical, cognitive, and emotional development. The impact of childhood trauma can persist into adulthood, influencing various aspects of individuals’ lives, including relationships, health, and mental well-being.
Childhood Trauma in Adults: Unraveling the Legacy
The legacy of childhood trauma often lingers into adulthood, shaping individuals’ beliefs, behaviors, and interpersonal relationships in complex ways. Adults who have experienced childhood trauma may grapple with challenges, including:
1. Emotional Dysregulation: Childhood trauma can disrupt the development of emotional regulation skills, leading to difficulties in managing and expressing emotions. Adults may experience intense mood swings, outbursts of anger or irritability, or feelings of numbness or detachment.
2. Attachment Issues: Trauma can impair the formation of secure attachment bonds, leaving individuals with insecure attachment patterns characterized by fear of abandonment, difficulty trusting others, and challenges in forming intimate relationships.
3. Self-Esteem and Identity: Childhood trauma can undermine individuals’ sense of self-worth and identity, leading to feelings of shame, self-blame, and worthlessness. Adults may struggle with low self-esteem, self-destructive behaviors, and a pervasive sense of inadequacy.
4. Physical Health: The effects of childhood trauma extend beyond psychological well-being to impact physical health. Adults with a history of trauma may be at increased risk for a range of health problems, including chronic pain, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease.
Types of Childhood Trauma: Understanding the Spectrum
Childhood trauma encompasses a diverse array of experiences, each with its unique manifestations and consequences. Common types of childhood trauma include:
1. Physical Abuse: Acts of physical violence or punishment inflicted upon a child by a caregiver or authority figure, resulting in bodily harm or injury.
2. Emotional Abuse: Verbal assaults, threats, or psychological manipulation aimed at undermining a child’s sense of self-worth and autonomy, often leading to emotional scars that endure into adulthood.
3. Sexual Abuse: Non-consensual sexual contact or exploitation of a child by an older or more powerful individual, causing profound psychological and emotional trauma.
4. Neglect: Failure to provide for a child’s basic needs, including food, shelter, supervision, and emotional support, leading to developmental delays, attachment issues, and impaired social functioning.
Navigating the Journey of Healing
Healing from childhood trauma is a complex and deeply personal journey that requires courage, compassion, and support. While the scars of trauma may never entirely disappear, individuals can cultivate resilience and reclaim agency over their lives through various therapeutic approaches, including:
1. Trauma-Informed Therapy: Evidence-based therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) can help individuals process traumatic memories, develop coping skills, and cultivate a sense of safety and empowerment.
2. Mindfulness and Self-Care: Practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and creative expression can provide avenues for self-discovery, self-compassion, and emotional regulation, fostering healing on a holistic level.
3. Supportive Relationships: Building and nurturing supportive relationships with trusted friends, family members, or mental health professionals can provide a vital source of validation, empathy, and connection on the journey toward healing.
Childhood trauma leaves an indelible mark on the lives of survivors, shaping their experiences, relationships, and sense of self in profound ways. By understanding the nature of childhood trauma, acknowledging its far-reaching effects, and embracing pathways to healing and resilience, we can create a more compassionate and supportive world where survivors can reclaim their voices, rewrite their stories, and thrive despite adversity.
_________________________________________________________________________________
Looking for treatment for an eating disorder, anxiety, depression, trauma, or postpartum mood disorder?
Evolve Counseling Services is a specialized team of Licensed Therapists providing treatment in Paoli.


